Competitive investors deliberate both bonds and stocks as effective asset strategies. Most of the investment-related articles also suggest equally investing in both assets. Even people often discuss stocks and bonds together while discussing investment. However, each has its pros and cons and thus growth differences. So then, why are they paired together?
One of the reasons is their frequent opposite movement, like the increase in stocks leads to a decrease in bonds and vice versa.
So, let’s dive deeper and learn comprehensively about what bonds and stocks hold in themselves and how it works.
Why do stocks and bonds move in inverse directions?
Stocks and bonds are relatively in correlation with each other as they move inversely. It usually becomes the investors’ primary concern because of the fear of losing shares in either investment strategy. However, you don’t need to be afraid yet only be diligent enough to track the change.
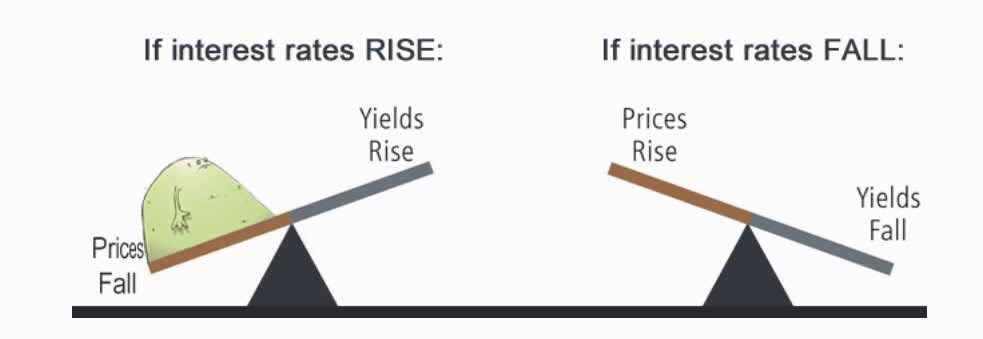
The reason behind this opposite relationship is that people mostly can’t buy stocks and bonds together. Therefore, when investors purchase stocks, it negatively affects the bonds rate and vice versa. As a result, people often sell their assets of stocks or bonds to get money for buying these assets.
Considering this, professional investors suggest investing in both, as it can neutralize the change, and you won’t have to suffer from possible inconveniences.
Difference between stocks and bonds
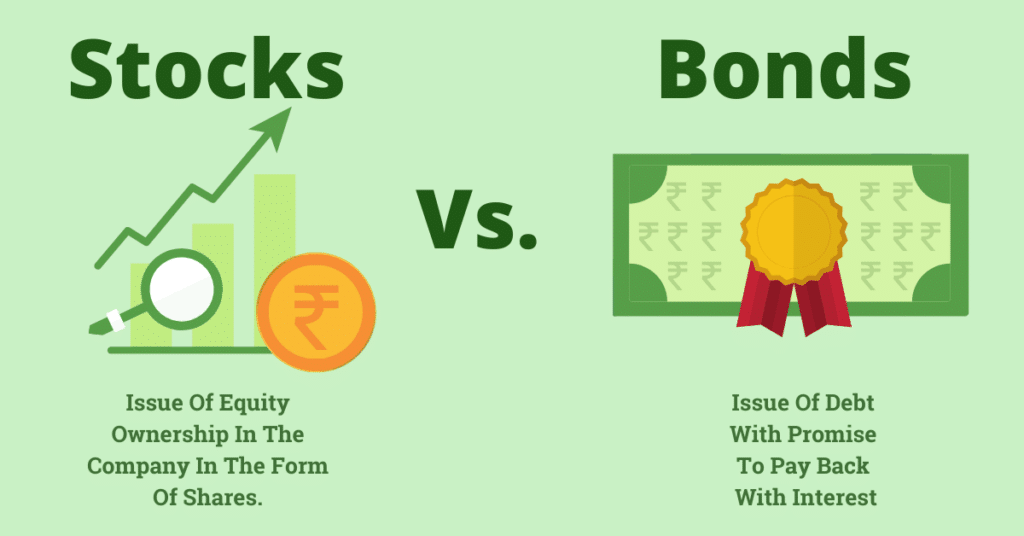
Let’s learn the basic difference between stocks and bonds.
Stocks
They refer to the financial share in the corporation that you can own by capitalizing a considerable amount.
For instance, if the stock rate per share is $50 and you have invested $2000 in stocks, you own 50% shares in a company. As the purchase of stocks, in actuality, means buying the part or slice of ownership of the company.
In this way, the company’s growth and decline become correlated to your financial status. Like, if the stock rate increases from $50 to $75, your initial investment value also increases automatically, and thus you can profit by selling the additional company shares.
The same goes with the loss. So you have to get ready for the decline in shares with the decline in stock prices.
Bonds
The provision of loan or funds to the companies or government generate bonds. Precisely, when you give a loan to a company in need, you get interest profit on it depending on the defined period until the company pays back the whole amount of which you purchase a bond.
For example, consider that you have purchased a $2500 bond on an annual interest rate of 2% for ten years. In this way, you earn nearly $500 interest or yield with your principal loan within the set time.
However, the risk arises when the company or government can’t pay the interest on your provided loan, or you can even lose your principal loan due to their bankruptcy.
Moreover, the interest rate and the duration of how long you can hold the bond depending on your purchased bond type.
Rules for deciding: comparing stocks and bonds
Should you know the principles of comparison, you will better choose between stocks and bonds.
Capital gains vs. fixed income
There is a significant difference in generating cash between these two. Stocks generate income through capital gains, and bonds own a fixed income. The investors earn capital gain by selling the companies or governmental shares at a greater price than the purchase amount. Then, you can either reinvest or spend it. Yet, it is not tax-deductible and depends on long or short-term gains.
Bond produces fixed income through interest rates.
For instance, you can earn profit for six months straight on treasury bonds until the company repays the loan. On corporate bonds, you can earn interest weekly or monthly, etc.
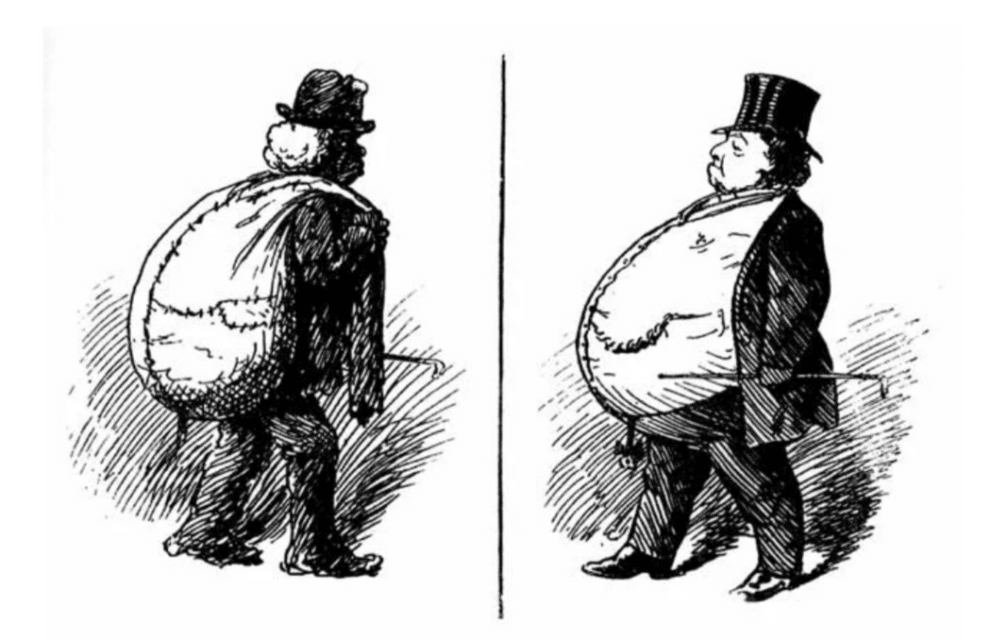
Equity vs. debt
The terms equity and debt refer to stocks and bonds, respectively. Financial equity is a US-based asset that can easily be converted into cash. The companies offer equity finance to investors to enhance their functioning by increasing the cash. Investors, in turn, grow with the growth in the company’s financial status.
In contrast, bonds or debt refer to the investing in debt under the condition that the company will pay it back with interest. You, in turn, gain partial shares in the company with the repaid loan and profit on it.
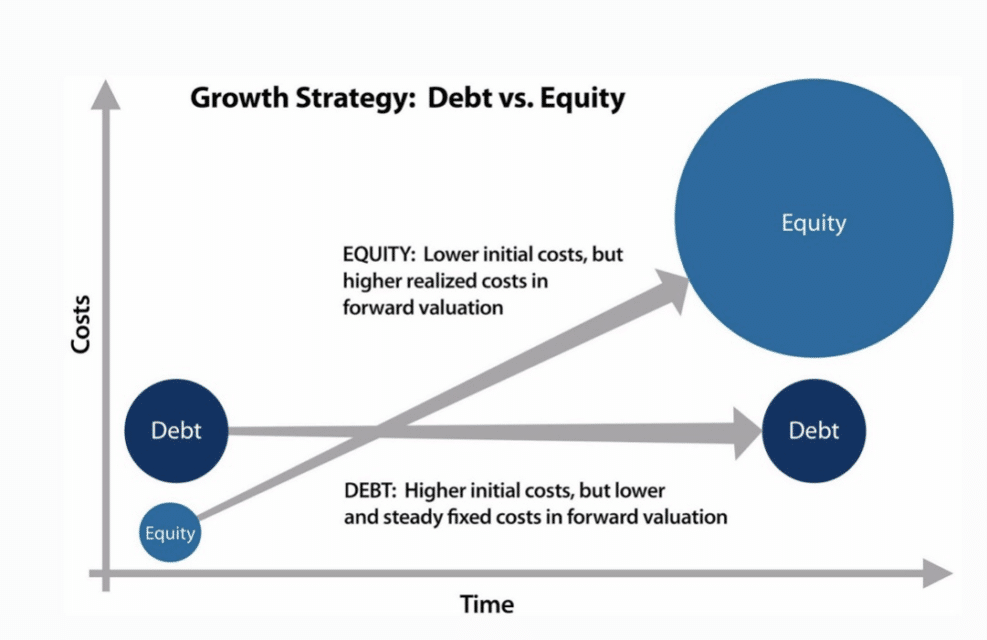
Performance
As mentioned above, the opposite relation also differentiates stocks and bonds from each other.
When the investors invest more in stocks, it marks an increment in stock gain and rates and, conversely, the demand or price of bonds decreases.
Bonds demand increases with the decline in the stock exchange, and stocks gain capital when the bonds are at risk.
Moreover, the performance of bonds also varies with lower and higher interest gains. Such as, the bond with a 2% yield becomes preferable as the new bonds may yield less interest.
Upsides and downsides of stocks and bonds
| Upsides | Downsides |
| Bonds are less prone to volatility thus are considered the safest investing activity. On the other hand, stocks are the most profitable long-term investment. | Stocks are more volatile than bonds. The issuance of bonds can negatively affect the provider’s financial condition as it is debt. |
| The gain profit ratio is higher in bonds as the rate of increment in interest price is higher. Therefore, investors can gain more advantage in stocks with economic growth. | In stocks, the rate of increment is lower on share’s profit. Likewise, the annual yield of bonds may decline with time. |
| Bonds are a diverse, effective, and profitable source of investment that also ensures the safety and comfort of the investors by assuring legality and offering different kinds of bonds. Stocks offer capital gain or growth on each sale. | Both stocks and bonds derive a higher risk rate as it entails efforts and proper research. |
Bonds or stocks: what is the best investment strategy?
Bonds and stocks both offer different benefits and risks. However, by summarizing the above points, we can say that bonds are much better for full returns. Moreover, as bonds offer fixed income, it is less prone to volatility and thus less risk.
Yet, when it comes to profit, stocks offer capital gain. So, although it is riskier, it offers more profitable returns.
However, considering the inverse relation, we will also suggest you invest in both short and long-term investments to reduce the chances of risk and earn more.
Final thoughts
Both of them are practical investing activities. They offer multiple benefits to their investors. Stocks offer shares or asset ownership in return for an investment of money. Bonds allow you to gain profit through interest by granting a loan.
However, as stocks and bonds move inversely, it is better to equally invest in both and generate profit when either of them is at its best.