Investing in bonds is a popular way to earn money from financial trading. This is because it has a better safety of investment and predictable income stream compared to the stock or currency market. However, you have to find the best way to grow your capital from different types of bonds.
Anyone who doesn’t have strong knowledge about the financial market can participate in bond trading. But before investing in bonds, an investor should know the drawbacks of the market with some basic knowledge about trading.
After completing this article, you will know which investment method is suitable for you.
How to invest in bonds: basics
We live in a world where borrowing money is a common thing. Bonds are simply a way of making money by borrowing, lending, and making profits from them. In that case, the borrower can be Govt, Corporate, and so on. Meanwhile, lenders can be individual investors, financial firms, banks, and so on.
Suppose your town asks you for money or creates offers to invest, by which they will make school, college, roads, hospitals or anything. They promise to pay you back your money with interest after a certain period. For example, you may invest $2000 in the bond and get $2200 with profit after six months. On the other hand, you can invest your $2000 in a target bond and collect a periodic interest that the issuer of the bond offers.
Understand your goal
Investing in bonds is secure than forex or the stock market. Although the return is low, bondholders get the priority when the company is in liquidation. Therefore, building your investment portfolio with lower risk and return bond trading would be perfect for you.
Prepare for risk and volatility
Although bonds are less risky — you cannot eliminate the risk at all. Moreover, returns that you will get from bond investment might not meet your needs. In that case, you should consider what risks and volatility are present in the bond market. You can minimize the risk as low as possible by following an investment management system.
Types of bonds
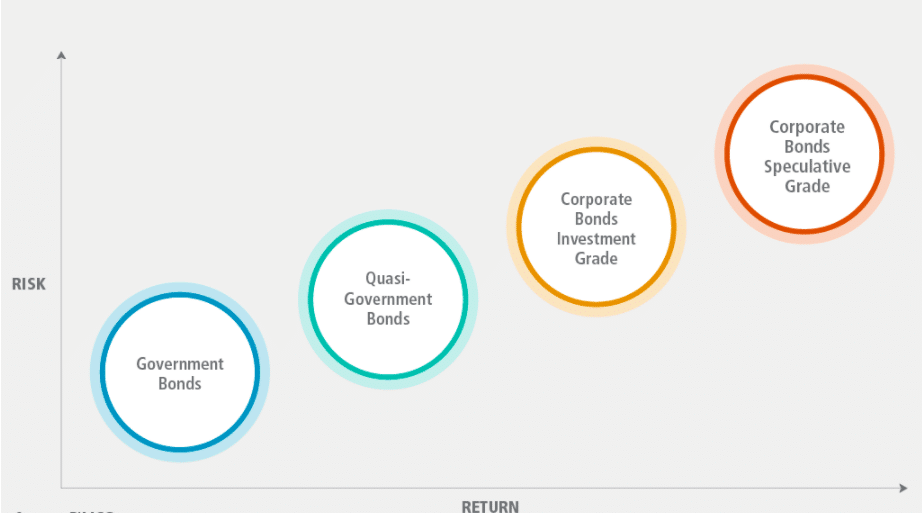
There are several types of bonds are available at the market, such as:
- Corporate bonds
The issuer of corporate bonds is large financial organizations to expand their business. The risk of investing in bonds depends on the issuing companies’ economic outlook, growth rate, and reputation. In some cases, there are convertible bonds you can find.
So the bonds that you can exchange with company stocks. However, investing in corporate bonds involves higher risks.
- T-bonds
The US department of treasury issues this highest security bond. The maturity date is 10 or 30 years for this type of bond. After reaching maturity, the bond will stop paying interest, and you get paid the worth of your investment and profit. You don’t have to pay tax for your investment at T-bonds interest, but default risk involves, so it offers less interest than corporate bonds. The US government backs T-bonds.
- Municipal bonds
The issuer of this type of bond is the local govt. This is to use the fund to do local development such as housing, roads, schools, etc. You may have tax-free interest from this type of bond, but the risk is involved as the local government often involves bankruptcy than the federal government.
Five ways to grow your capital from bonds
Let’s make a list of ways to grow capital from bonds.
- Collecting interest
With this investment, you will purchase bonds that you prefer. Then wait until the bonds mature and collect the interest payment that the issuer offers on them. Bond interest generally pays interest twice a year. You need to purchase and wait until the bond is mature to generate interest in this type of investment.
For example, you may invest $1000 in some bonds at a 4% interest rate, which will pay interest twice a year. After a year, you can withdraw the 8% interest of your capital, or some allow reinvestment so you can reinvest also.
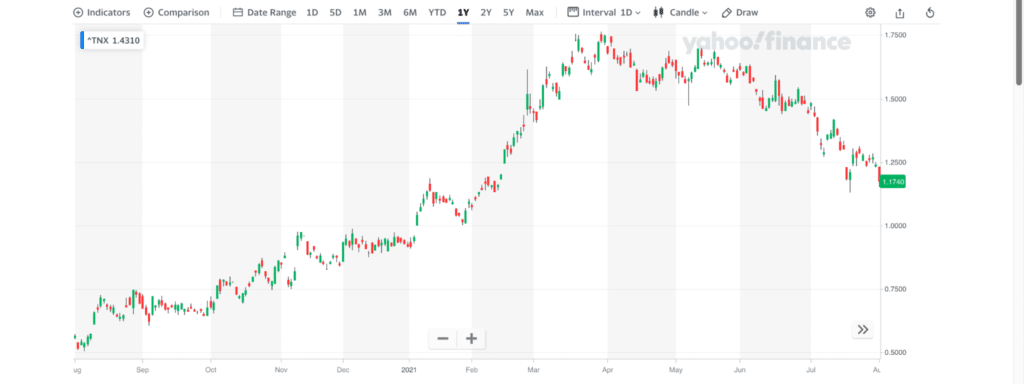
The above image shows the US 10 year treasury that provides a 0.5% interest rate, just above the poverty level.
- Making frequent trade
The second way from investing in bonds is making frequent trades like other tradable assets. You purchase a bond and wait until it increases in value, then sell it.
For example, you buy a bond worth $1500, and after two months, the value rises to $1700. You sell the bond with a net $200 profit. You have to be aware that bond markets are often less volatile than stocks or currency markets.
- Fundamental
You can make money from the bond market by following fundamental facts.
For example, if you purchase T-bonds, you keep an eye on news and events related to the interest rates from the Federal Reserve. Interest rate affects the T-bond market. Similarly, there are so many fundamental facts that affect bond prices.
- Swing positions
You can see the bond price in the chart like stocks, currency pairs, and commodities if you know about technical trading and research on the bond market. You can easily make swing positions on the target bond price and grow your capital from it. This type of investment requires enough research and knowledge to make money.
- Price action
Another way to grow capital from the bond market is by investing in bonds by following price action. We know the price action trading is effective for any tradable asset to large financial institutions. So smart investors frequently follow price action to make any investment or trade. The economic organization issues every type of bond, so investing in price action is an excellent investment method.
Final thoughts
Finally, we know all the basic things that any novice needs to understand before investing in bonds. When investors start to invest in bonds, they face some issues or drawbacks involved in the bond investment.
Drawbacks such as smaller returns and less transparency are common in bond investment. For long-term investment, you put away your capital for a more extended period. The standard-issue comes up in bond investment, such as the source of purchase.
You can purchase it from brokers and also directly from another owner or issuer. When buying it from brokers, they offer a higher price to buy than the regular market value.




